Arif, M, Triyono, S, & Sahayu, W (2018). Pinkfong stories in extending utterances to young Indonesian EFL learners: A case study. Applied Linguistics Research Journal, 4(2), 15-24.
Chen, Z (2006).
The effects of multimedia annotations on L2 vocabulary immediate recall and reading comprehension: A comparative study of text-picture and audio-picture annotations under incidental and intentional learning conditions (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of South Florida: Florida:Retrieved from
https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3477&context=etd.
Educational Testing Service [ETS] (2018a). TOEIC official test preparation book LC. Seoul:YBM.
Educational Testing Service [ETS] (2018b). TOEIC official test preparation book RC. Seoul:YBM.
Hsieh, Y, & Huang, S (2020). Using an e-book in the secondary English classroom: Effects on EFL reading and listening.
Education and Information Technologies,
25(2), 1285-1301.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-10036-y.

Kalyuga, S (2000). When using sound with a text or picture is not beneficial for learning.
Australian Journal of Educational Technology,
16(2), 161-172.
https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.1829.

Karbalaei, A, & Zare, A (2019). A comparison of the effect of textual, audio and textual-pictorial and audio-pictorial annotations on enhancing reading comprehension among Iranian EFL learners.
Teaching English with Technology,
19(3), 40-67. Retrieved from
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1224608.pdf.
Kim, N-Y (2019). Effects of captioning order on EFL listening and reading: Should captions be first or second?
English Language and Literature Teaching,
25(4), 1-22.
https://doi.org/10.35828/etak.2019.25.4.1.

Kosal, İ (2008). Enhancing writing and improvisational speaking skills through fairy tales in EFL preparatory classrooms (Unpublished doctoral dissertation) Selçuk University, Konya, Turkey.
Liu, H, Cao, S, & Wu, S (2019). An experimental comparison on reading comprehension effect of visual, audio and dual channels.
Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology,
56(1), 716-718.
https://doi.org/10.1002/pra2.148.

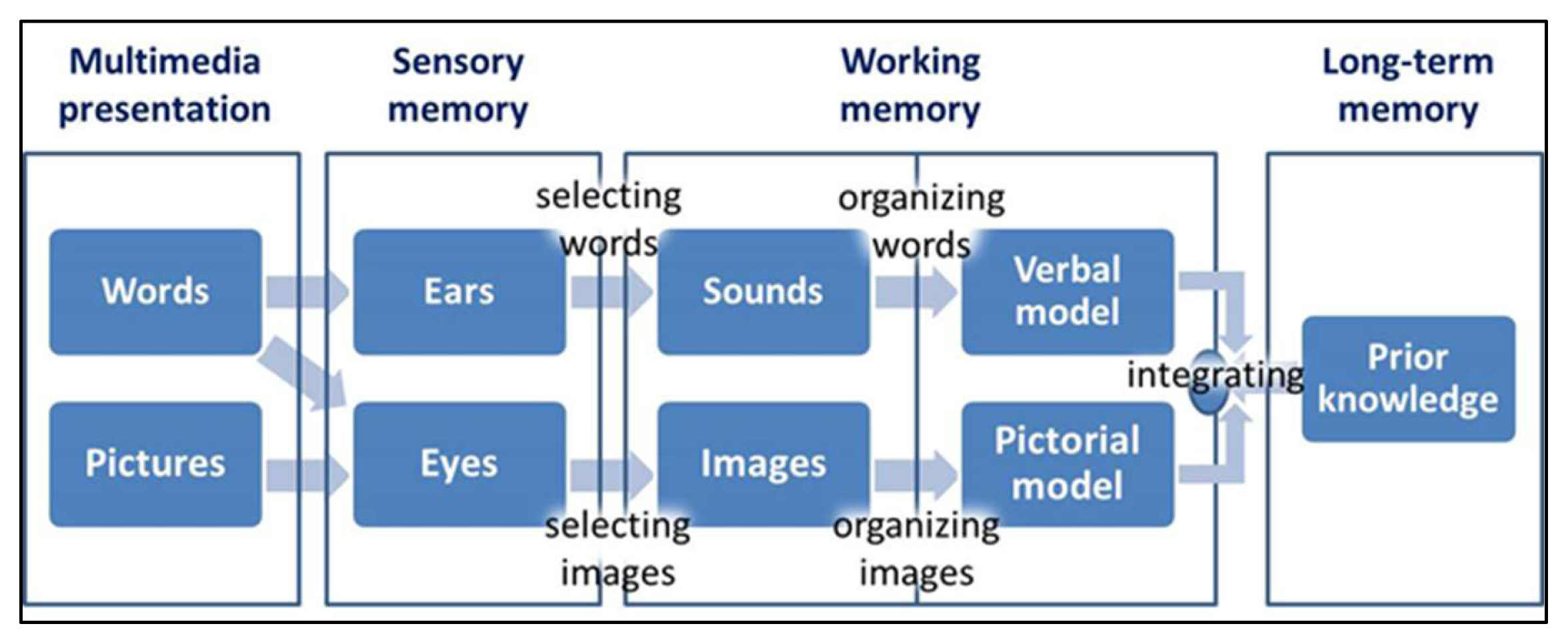
Mayer, RE (2005). Cognitive theory of multimedia learning. In RE Mayer (Ed.),
The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning. pp 31-48. New York, NY:Cambridge University Press:
https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511816819.

Mayer, RE, Heiser, J, & Lonn, S (2001). Cognitive constraints on multimedia learning: When presenting more material results in less understanding.
Journal of Educational Psychology,
93, 187-198.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.93.1.187.

Mohamed, MMK (2018). Using audiobooks for developing listening comprehension among Saudi EFL preparatory year students.
Journal of Language Teaching and Research,
9(1), 64-73.
https://doi.org/10.17507/jltr.0901.08.

Moyer, JE (2011).
Teens today don’t read books anymore: A study of differences in comprehension and interest across formats (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Minnesota: MN:Retrieved from
https://hdl.handle.net/11299/116037.
Rogowsky, BA, Calhoun, BM, & Tallal, P (2016). Does modality matter? The effects of reading, listening, and dual modality on comprehension.
SAGE Open,
6(3), 1-9.
https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244016669550.

Samsung Publishing Company (2020). The world’s best fairy tales in English (5th ed). Seoul:Samsung.
Sorden, SD (2005). A cognitive approach to instructional design for multimedia learning.
Informing Science,
8, 263-279.
https://doi.org/10.28945/498.

Suvorov, R (2009).
Context visuals in L2 listening tests: The effects of photographs and video vs audio-only format (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Iowa State University: Ames, Iowa:Retrieved from
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/38911438.pdf.
Sweller, J (2005a). Cognitive theory of multimedia learning. In RE Mayer (Ed.),
The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning. pp 19-30. New York, NY:Cambridge University Press:
https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511816819.

Sweller, J (2005b). The redundancy principle in multimedia learning. In RE Mayer (Ed.),
The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning. pp 159-168. New York, NY:Cambridge University Press:
https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511816819.011.

Turker, S (2010).
The effectiveness of audio books on the reading comprehension of selected texts by university EFL students at different proficiency levels (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Bilkent University: Ankara, Turkey:Retrieved from
https://www.thesis.bilkent.edu.tr/0003964.pdf.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print